| WHAT IS PROPULSION? | ||
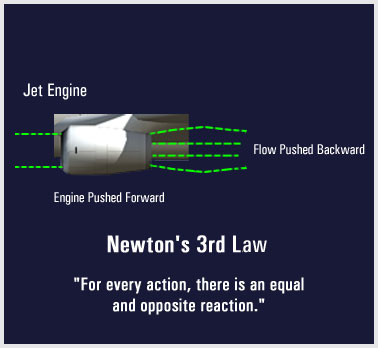
To summarize, the mathematical basis of propulsion theory was first stated in the 17th century. It was then that Isaac Newton formulated his three Laws of Motion. In particular, it was Newton’s third law that captured the essence of rocket propulsion: For every action in nature there is an equal and opposite reaction. To restate this law in terms of basic rocket propulsion theory, when gasses created by fuel combustion escape out the rear of a rocket (action), the result is a push in the opposite direction (reaction). |
|
|
| 16 of 39 | ||