| PARALLEL CIRCUITS | ||
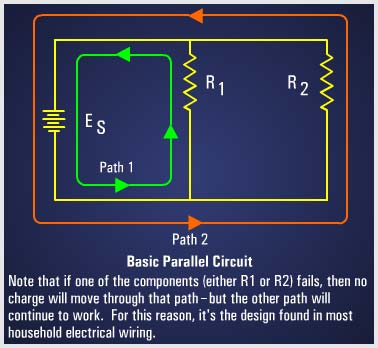
A parallel circuit has more than one resistor and gets its name from having multiple (parallel) paths to move along. Charges move through any of several paths. Parallel circuits, therefore, must contain two or more resistances which are not connected in series. Starting at the voltage source (ES), trace counterclockwise around the circuit. Two complete and separate paths can be identified in which current can flow. One path is traced from the source, through resistance R1, and back to the source. The other path is from the source, through resistance R2, and back to the source. |
|
|
| 11 of 61 | ||