| THE FUNDAMENTAL CONCEPTS - ELECTRICAL CONDUCTIVITY | ||
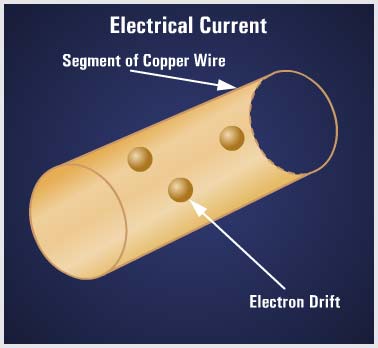
The electrical conductivity of matter depends on the atomic structure from which the conductor is made. In a solid material such as copper, the atoms that make up the molecular structure are bound firmly together. At room temperature, copper contains a considerable amount of heat energy. Since heat energy is one method of removing electrons from their orbits, copper has many free electrons that move from atom to atom. Under the influence of electric force, the electrons move generally in the same direction. The effect of this drifting is felt almost instantly from one end of the conductor to the other. This electron movement is called an ELECTRIC CURRENT. |
|
|
| 13 of 67 | ||