| CURRENT | ||
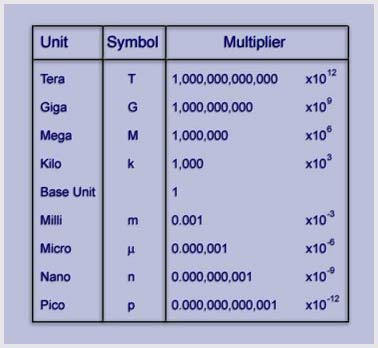
Electric current is defined as the directed movement of electrons and the term ‘current flow’ is most commonly used to denote this directed movement. The magnitude of current is measured in AMPERES. A current of one ampere is said to flow when one coulomb of charge passes a point in one second. Remember, one coulomb is equal to the charge of 6.28 x 1018 electrons. Frequently, the ampere is much too large a unit for measuring current. Therefore, the MILLIAMPERE (mA), one-thousandth of an ampere, or the MICROAMPERE (µA), one-millionth of an ampere, is often used. |
|
|
| 19 of 67 | ||