| THE FUNDAMENTAL CONCEPTS - INSULATORS AND SEMICONDUCTORS | ||
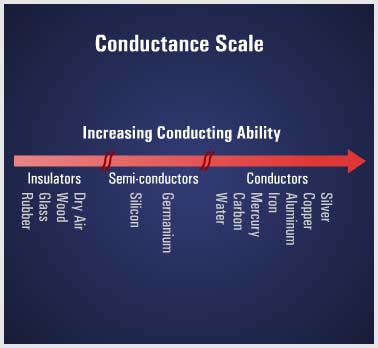
Since their atoms hold their electrons tightly, nonconductors, or insulators as they are called, have very few free electrons and strongly oppose (or resist) their ‘flow’. Some examples of these materials are rubber, plastic, enamel, glass, dry wood, and mica. Just as there is no perfect conductor, neither is there a perfect insulator. Some materials are neither good conductors nor good insulators, since their electrical characteristics fall between those of conductors and insulators. These in-between materials are classified as semiconductors. Germanium and silicon are two common semiconductors used in solid-state devices. |
|
|
| 15 of 67 | ||