| POWER | ||
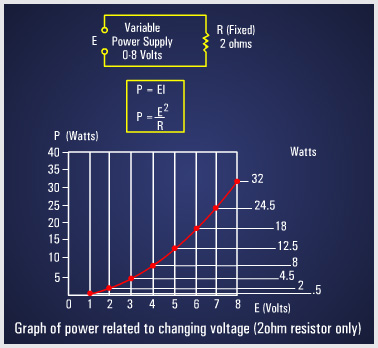
Power in watts is equal to the voltage across a circuit multiplied by current through the circuit. This represents the rate at any given instant at which work is being done. The symbol P indicates electrical power. Thus, the basic power formula is P = E x I, where E is voltage and I is current in the circuit. The amount of power changes when either voltage (E) or current (I), or both voltage and current, are caused to change. |
|
|
| 29 of 67 | ||