| THE FUNDAMENTAL CONCEPTS - ATOMIC NUMBER | ||
Elements are classified numerically according to the complexity of their atoms. The atomic number of an atom is determined by the number of protons in its nucleus. In a neutral state, an atom contains an equal number of protons and electrons. Therefore, an atom of hydrogen - which contains one proton and one electron - has an atomic number of 1; while helium with two protons has an atomic number of 2. In addition, helium has two electrons and two neutrons. The complexity of atomic structure increases with the number of protons and electrons. |
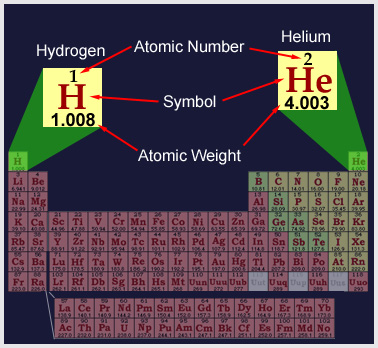
|
|
| 5 of 67 | ||