| CURRENT - ALTERNATING CURRENT | ||
Alternating current (AC) is current which, unlike DC, constantly changes in amplitude, and which reverses direction at regular intervals. Unlike direct voltages, alternating voltages can be stepped up or down in amplitude by a device called a transformer. Use of the transformer permits efficient transmission of electrical power over long-distance lines. Due to its inherent advantages and versatility, AC has replaced direct current in all but a few commercial power distribution systems. |
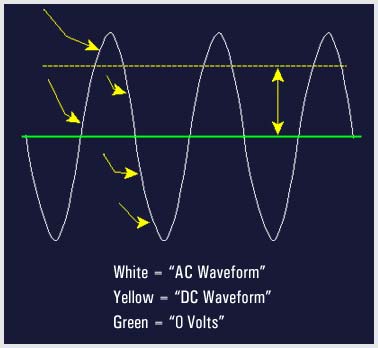
|
|
| 22 of 67 | ||